The Electronic Trip Unit (ETU) of air circuit breakers serves as the brain of the system, providing advanced protection and control functionalities. By integrating electronic components, the ETU enhances the performance and reliability of air circuit breakers.
It offers precise monitoring of electrical parameters, such as current, voltage, and frequency, enabling rapid response to faults and overloads.
Additionally, the ETU enables customizable settings for trip curves and protection coordination, ensuring optimal operation tailored to specific application requirements. With its advanced features and flexibility, the ETU plays a crucial role in safeguarding electrical systems and maximizing operational efficiency.
The protection functions of the electronic trip unit are available without an additional auxiliary voltage. The required energy is supplied via current transformers integrated in the Circuit Breaker.
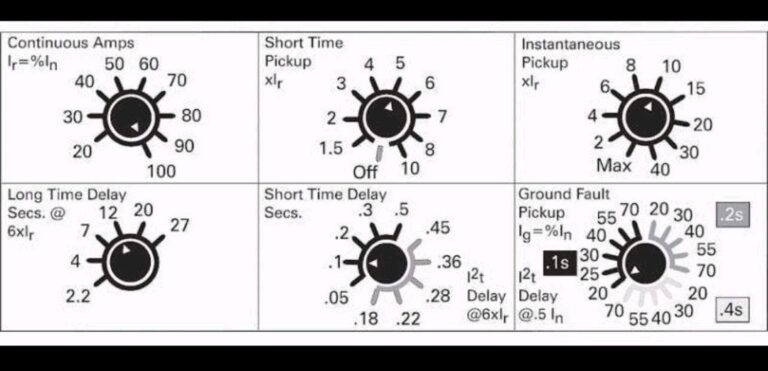
To evaluate the currents, the RMS value is calculated by the electronic components of the electronic trip unit. The individual functions are parameterized by means of rotary coding switches.
- Ir (Rated Current): This parameter represents the rated current of the circuit breaker, which is the maximum continuous current that the circuit breaker is designed to carry without tripping under normal operating conditions.
- Isd (Short-time Delay Current): Isd is the current threshold above which the circuit breaker will trip after a short delay. This delay is typically designed to allow for temporary overcurrent conditions, such as inrush currents during motor starting, without tripping the breaker.
- li (Instantaneous Current): li is the current threshold at which the circuit breaker will trip instantaneously, without any delay. This parameter is used to provide rapid protection against short-circuit faults that require immediate interruption of current flow.
- Ig (Ground Fault Current): Ig represents the current threshold for detecting ground faults, which occur when an unintended electrical connection occurs between an energized conductor and a grounding surface. Ground fault protection is essential for safety and preventing electrical hazards.
- tr (Tripping Time): Tr represents the time it takes for the circuit breaker to trip once the current exceeds the designated threshold. It includes both the delay time for short-time tripping (if applicable) and the instantaneous tripping time.
- tsd (Short-time Delay Time): Tsd is the delay time associated with short-time tripping. It determines how long the circuit breaker will allow the current to exceed the short-time delay current before tripping.
- tg (Ground Fault Delay Time): Tg is the delay time associated with ground fault protection. It specifies the time delay between detecting a ground fault and tripping the circuit breaker to isolate the faulted circuit.
These parameters are crucial for configuring the protection settings of the circuit breaker to ensure reliable and selective operation under various fault conditions while minimizing unnecessary tripping and downtime. Users can adjust these parameters according to the specific requirements of their application and the characteristics of the electrical system being protected.