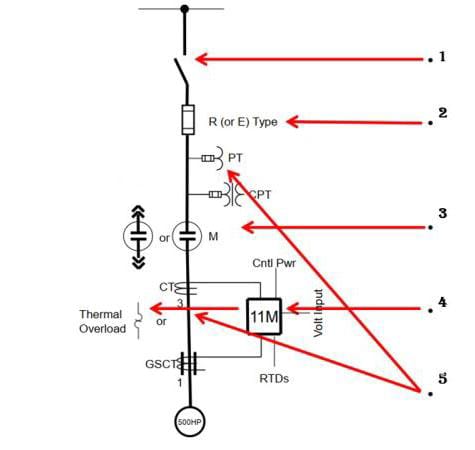
1. Isolation Switch
• Quick-Make, Quick-Break, Non-Load Break, Isolation Switch.
• Safety device to isolate fuses/contactor from main bus
• Manually-operated
• Interlocks Prevent
> Operation when contactor closed (motor energized)
> Opening door when switch is closed (must be fully off)
> Accidental operation when HV door is open
2. Power Fuse
• Type R fuses are used for motor applications and General Purpose type E fuses are used for transformer/feeder applications.
• MV E2 motor controllers use current-limiting back-up fuses which provide the short-circuit protection for the motor and motor controller.
• Fuses must be coordinated with the contactor and O/L relay for proper MV E2 motor controller applications.
• The MV fuses must permit repetitive switching of the load while taking into consideration the magnitude of inrush current and associated time without damage to the fuse.
3. Vacuum Contactor
• Vacuum contactor switching device
• Stationary or Draw-out construction available
Standard Electrically (magnetic) held, or Optional mechanically(latched) held available.
Max Voltage: 2400V-7200V (higher voltage ratings may be available and/or MV breakers may be used for applications higher than 7200V)
200A, 400A, and 800A nominal ratings (deratings may apply for enclosure type, configuration, altitude, ambient temperature, etc.)
4. Instrument Transformers
• CTs: Standard Window type or optional Bar type phase CTs are available. Optional window type GSCT available.
• Standard CTs used in MV MCCs are normally single ratio and have a relatively low Accuracy Class, e.g. C10 (window) or T50 (bar). Multi-ratio and higher CT accuracy classes are available, but may require additional sections or space, due to size to accommodate mounting.
• PTs: Optional stationary mounted in starter compartments are available in open-delta, or wye connected configurations, but may require additional space to accommodate mounting.
5. Overload Relay
If the motor drives a load that’s too heavy or gets jammed, it draws more current than its rated value. Over time, this overcurrent causes overheating, which can damage the motor windings.
Overload relays detect this slow rise in current and trip the motor before it gets damaged.