If you closely observe inside electrical panels you will notice your bus bars ; which is used to flow current inside panel rather than a cable are is shape of rectangular . Most of them are cu bus bars.
Electrical bus bars are typically rectangular rather than circular for several practical and technical reasons:-
1. Current Distribution: –In a conductor, current tends to flow near the surface due to the “skin effect” at higher frequencies. A rectangular cross-section provides a larger surface area for current flow, making it more efficient for conducting large currents compared to a circular cross-section.
2. Space Efficiency: Rectangular bus bars can be stacked or placed side by side in compact spaces, maximizing the use of available room within electrical panels or switchgear. Circular conductors would leave gaps and take up more space.
3. Cooling Efficiency: A rectangular shape allows for better heat dissipation. Its larger flat surfaces can be exposed to air or cooling systems, enhancing heat transfer compared to the limited surface area of a circular conductor.
4. Mechanical Stability: Rectangular bus bars are more rigid and less likely to bend or twist under mechanical stress, making them more suitable for large installations where stability is important.
5. Ease of Fabrication: Rectangular bus bars are easier to manufacture, handle, and install, especially when precise bends or custom configurations are required.These factors make the rectangular shape more practical for high-power electrical applications where efficient current handling, space, and cooling are critical.
They come in different sizes bus bar calculation is a must before designing a panel . Each bus bars have different types of current carrying capacities. Usually the current carrying capacity of the bus bar is considered = 1.2 * width mm * depth mm
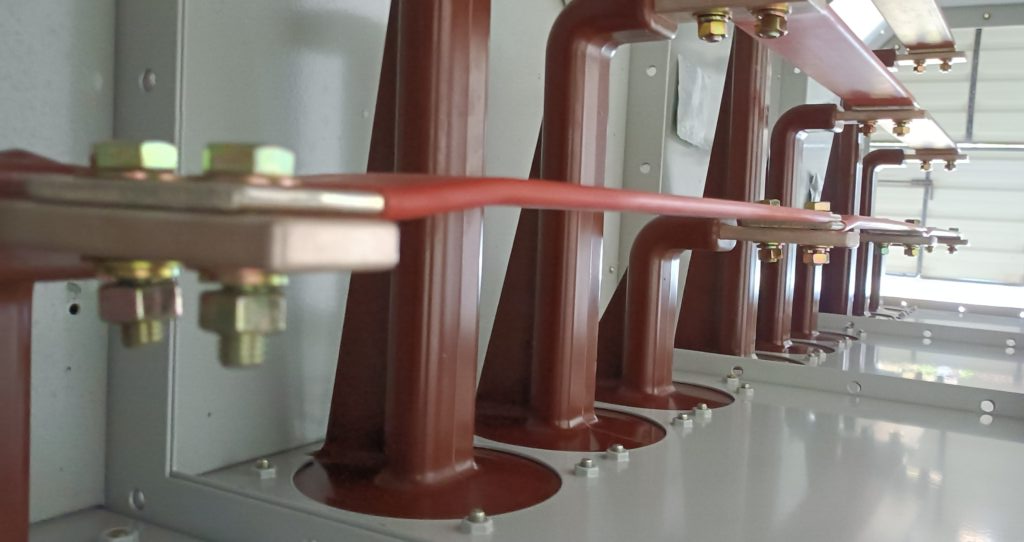

Panel Bus Bar