Winding Resistance and Turn Ratio Testing in Power Transformers In the maintenance of power transformers, two critical tests stand out:-
Winding Resistance Testing (WRT) and Transformer Turns Ratio (TTR) Testing.
1. Winding Resistance Testing (WRT):-
WRT is essential for detecting issues like loose connections, damaged windings, or other electrical faults within a transformer. By measuring the resistance of the windings, we can ensure the health and efficiency of the transformer, which is crucial for optimal performance and reducing downtime.
🎯 Goal:-
The goal of winding resistance testing is to ensure uniformity across the windings and identify any irregularities such as poor contacts, loose connections, or winding damage, which can lead to efficiency loss and potential failure.
✅ Acceptable Values:-
Winding resistance values should be balanced between phases and within ±5% of the factory specification or previous test results.
Reference: IEEE Standard C57.12.90-2015, which provides guidelines for performing winding resistance measurements.
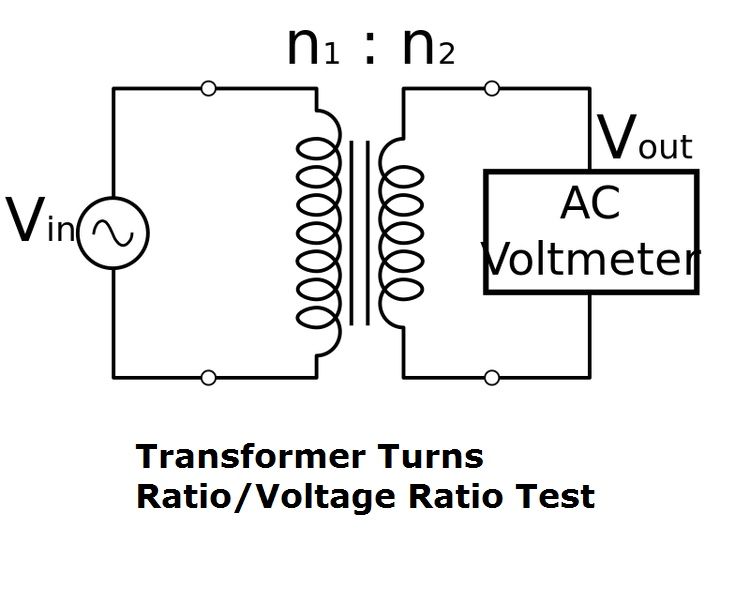
2.Transformer Turns Ratio (TTR) Testing:
TTR testing ensures the transformer’s voltage ratio is consistent with its design. This test helps identify problems like shorted turns, incorrect winding connections, or core issues, which can significantly impact the transformer’s functionality.
🎯 Goal: The goal of TTR testing is to verify that the transformer is stepping voltage up or down correctly according to its design. Any mismatch can indicate winding damage or other internal faults that could impair the transformer’s operation.
✅ Acceptable Values: The transformer’s turn ratio should be within ±0.5% of the calculated value based on the transformer’s nameplate ratings.
Reference: IEEE Standard C57.12.00-2010, which specifies TTR testing procedures for transformers. Both of these tests are indispensable in predictive and preventive maintenance strategies. They help maintain transformer reliability, extend its lifespan, and prevent costly failures.