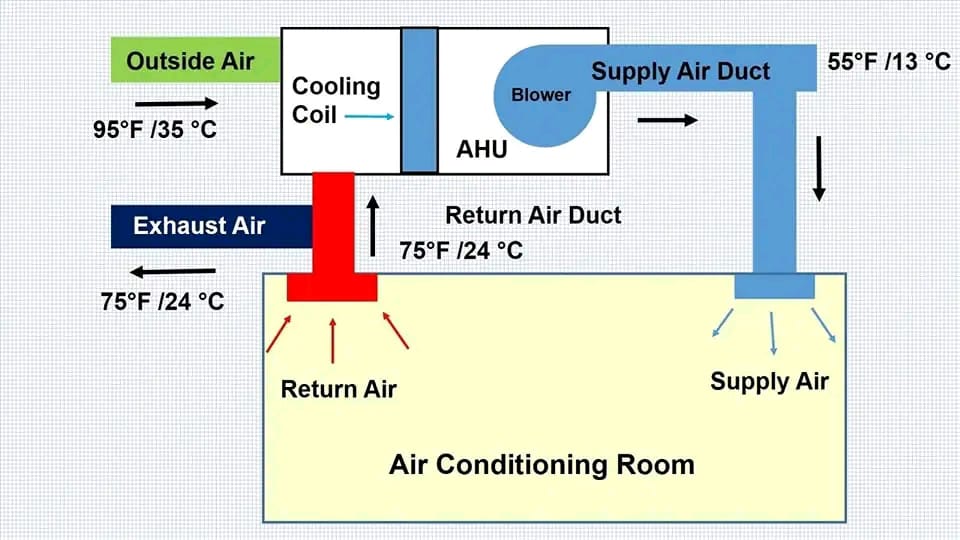
Difference between Supply Air l Return Air l Exhaust Air & Fresh Air …?
The terms supply air, return air, exhaust air, and fresh air are commonly used in heating, ventilation, and Air conditioning (HVAC) systems.
Here are the differences:-
1. **Supply Air:**
– **Definition:** Air that is distributed from the HVAC system into the conditioned space.
– **Function:** It delivers heated or cooled air to maintain the desired indoor temperature and air quality.
– **Path:** Typically moves from the HVAC unit through ducts and vents into various rooms.
2. **Return Air:**
– **Definition:** Air that is drawn from the conditioned space back into the HVAC system.
– **Function:** It returns indoor air to the HVAC unit to be reconditioned (heated, cooled, filtered) and recirculated.
– **Path:** Travels from rooms through return ducts and vents back to the HVAC unit.
3. **Exhaust Air:**
– **Definition:** Air that is expelled from the building to the outside.
– **Function:** It removes stale, contaminated, or excess air from the indoor environment to improve air quality.
– **Path:** Typically extracted from areas like bathrooms, kitchens, or other spaces where air quality is compromised and directed outside through exhaust ducts and fans.
4. **Fresh Air:**
– **Definition:** Outdoor air that is brought into the building.
– **Function:** It introduces outside air into the indoor environment to dilute indoor pollutants and replenish oxygen levels.
– **Path:** Enters the building through fresh air intakes, often filtered and conditioned by the HVAC system before mixing with the indoor air.
In summary:-
**Supply Air**: Air delivered to indoor spaces from the HVAC system.-
**Return Air**: Air taken back to the HVAC system from indoor spaces.-
**Exhaust Air**: Air expelled from the building to the outside.-
**Fresh Air**: Outdoor air brought into the building for ventilation.
#HVAC