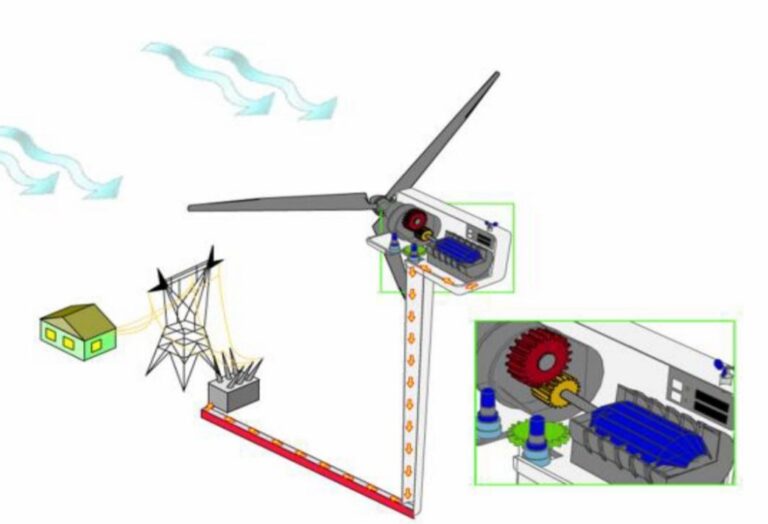
How The Electricity deliver to our homes ?
Delivering the electricity divided into 8 simple steps from a generator to loads (like homes and businesses):
1. Generation 11 KV:-
– A generator produces electricity by converting mechanical energy (often from wind, water, or steam) into electrical energy.
2. Step-Up Transformer 11 KV / 132 KV, 220 KV and 400 KV:-
– The generated electricity is sent to a step-up transformer. This device increases the voltage of the electricity, allowing it to travel long distances more efficiently.
3. Transmission Lines 132 KV, 220 KV and 400 KV :-
– The high-voltage electricity travels through transmission lines. These are large cables that carry electricity over long distances from power plants to substations.
4. Substation 132 KV, 220 KV and 400 KV / 33 KV:-
– When the electricity reaches a substation, it goes through a step-down transformer. This reduces the voltage to a safer level for distribution.
5. Distribution Lines 33 KV / 11 KV:-
– The lower-voltage electricity is sent through distribution lines. These lines carry electricity to neighborhoods and businesses.
6. Service Transformer 11 KV / 415 V:-
– Near homes or businesses, a service transformer further reduces the voltage to a usable level (240 volts).
7. Electric Meter:-
– The electricity passes through an electric meter, which measures how much electricity is used.
8. Loads:-
– Finally, the electricity reaches the loads (like lights, appliances, etc.), providing the power needed for everyday activities.
#T&D #transmission and Distribution