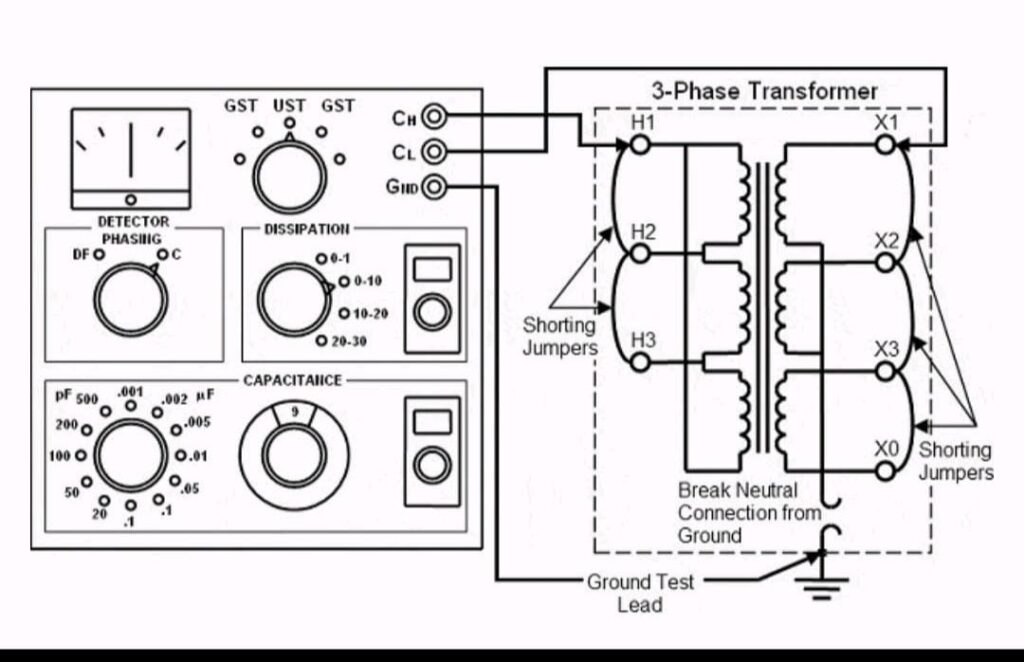
Transformer Tan Delta Test
The Transformer Tan Delta Test (often called the Tan Delta Test or Power Factor Test) is a diagnostic test used to assess the insulation quality of transformers and other electrical equipment. This test measures the power factor or dissipation factor (tan δ) of the insulation material, which helps indicate the condition of the insulation.
Points about the Tan Delta Test:
- Purpose: The test is used to identify insulation degradation, moisture presence, and other issues that may affect the reliability and performance of transformers.
- Measurement: During the test, an 10k voltage is applied to the transformer, and the current flowing through the insulation is measured. The tangent of the delta (tan δ) is calculated by comparing the resistive and capacitive currents.
- Interpretation:
A low tan δ value indicates good insulation quality.
An increasing tan δ value over time can indicate deteriorating insulation, which may require further investigation or maintenance. - Frequency: The test is typically conducted at power frequency (50/60 Hz) and can also be performed at higher frequencies to gain more insights into the insulation condition.
The Tan Delta Test is an essential part of preventive maintenance programs for electrical equipment, helping to ensure the reliability and safety of transformers in operation.