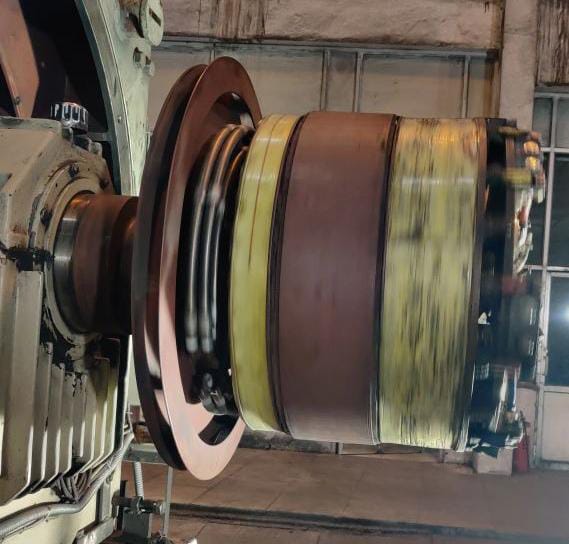
Discharge resistors in an alternator are used to dissipate stored electrical energy safely and quickly when the excitation system is turned off. They are mainly found in alternators that use PMG (Permanent Magnet Generator) excitation systems and brushless excitation systems.
Key functions of discharge resistors in an alternator
1. Safe dissipation of stored energy in the excitation circuit
– In brushless alternators, the rotor winding and rotating diodes store electrical energy when the machine is running.
– When the excitation is suddenly removed (e.g., during a shutdown or trip condition), this stored energy can cause high voltage spikes, potentially damaging the excitation system components.
– A discharge resistor helps by quickly dissipating this energy, preventing overvoltage stress on diodes and insulation.
2. Protection of rotating diodes
– Alternators with a rotating diode bridge use discharge resistors to prevent reverse voltage stress on the diodes during shutdown.
– Without a discharge resistor, the sudden voltage collapse could lead to diode failure due to excessive reverse current.
3. Prevention of voltage surges in the field circuit
– The field circuit (rotor winding) behaves like an inductor, meaning it resists sudden changes in current.
– When excitation is turned off, the collapsing magnetic field can induce a high voltage spike (Lenz’s Law).
– The discharge resistor provides a path for this excess current, preventing insulation breakdown or arcing in the excitation circuit.
4. Faster de-excitation of the alternator
– Without a discharge resistor, the field winding would take longer to de-energize, delaying the alternator shutdown.
– The resistor speeds up the de-excitation process, making shutdowns more controlled and safe.
Typical placement of discharge resistors in an alternator
– Connected across the field winding (rotor circuit) in parallel.
– In series with the excitation circuit to absorb excess energy.
– Across the rotating diode assembly to protect against transient voltages.
Conclusion:-
Discharge resistors in an alternator are crucial for the safe dissipation of stored electrical energy in the excitation system. They protect rotating diodes, prevent voltage surges, ensure quick de-excitation, and enhance the overall reliability of the alternator.